Vitreo Retinal services
We have 18 years of the Best Experience in Retina Services
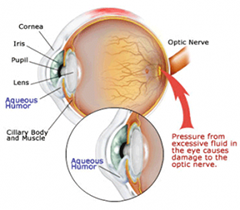
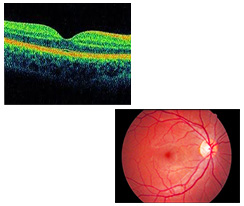
Understanding the Retina
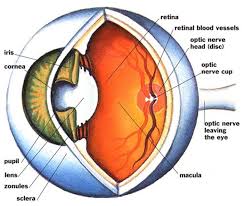
Retina is the light-sensitive layer in the back of your eye. It contains millions of special nerve cells that react to light. These photoreceptors send electrical impulses to your optic nerve, which your brain converts into the images you see. Any damage to the retina can have irreversible loss of vision. All the retinal diseases need extremely careful treatment and regular monitoring may be necessary till the condition heals. Early diagnosis and treatment is advised in all the retinal diseases.
Retinal diseases which leads to blindness
- Age-related Macular degenerations (AMD),
- Diabetic Retinopathy
- Retinal Detachments due to myopia (short sightedness)
- Vascular disorders - retinal vein occlusion, hypertensive retinopathyretinal artery occlusion, Vasculitis etc.,
- Macular hole, Epi-retinal membranes, Vitreo-macular traction etc
How Vitreo Retinal Surgeries are conducted in Bangalore Nethralaya?
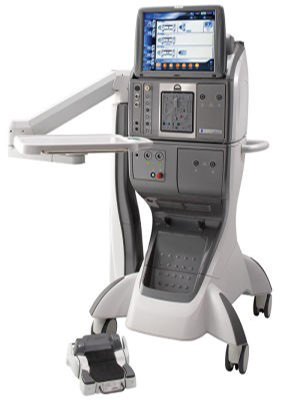
Constellation vision system
Modern vitreo-retinal surgery is simply inseparable from cutting-edge technology — pun intended. From some of the earliest innovations in applied medical optics, such as slit lamps, binocular indirect ophthalmoscopes, and argon laser, all the way to today’s advanced vitrectomy machines, spectral OCT, and bionic retinal prostheses, modern vitreo-retinal surgery has always pushed the development of biomedical technology, and advances in technology have always driven advances in vitreo-retinal surgery. An important driver for this change has been developing technology.
We are fully equipped with world-class technology like latest cordless Indirect ophthalmoscopes, fluorescein & indocyanin green digital angiography, spectral SLO OCT & Carl Zeiss HD OCT to help our ‘best expertise’ for the diagnosis of various retinal conditions. For the best management we have world class Iridex Green Lasers, latest micro-pulse & multi-spot pattern lasers, 23/25/27G Alcon’s Constellation Vitrectomy vision system & high end surgical microscope with BIOM viewing system.
Our Constellation vitrectomy machine is the best & latest in the world for MIVS (Micro-Incision Vitrectomy Surgical procedure) with exceptional level of performance in high speed surgical control, integrated pressurized infusion & IOP compensation with advanced & safe xenon illumination. The healing is much faster & the post-operative comfort is extremely good with MIVS procedure and it is completely changed the way vitreo-retinal procedures were performed earlier.
Evaluation of a patient at our retina clinic
Important Retinal Conditions
Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) is one of the foremost frequent causes of blindness world-wide. In India, it was the 17th cause of blindness 25 years ago but has now ascended to the 5th position. It is estimated about 70-80 million people are affected by diabetes in India, the largest number in any nation in the world. It is estimated that 15 to 25% of the diabetic population have diabetic retinopathy, and everyone has the potential to develop it over a period of time. More than 75% of patients who have diabetes mellitus for more than 20 years will have some form of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetic Retinopathy is symptomless in its early stage; screening is the only way to identify these patients to prevent them from going blind.
Awareness of the disease and of its treatment modalities among the community and physicians is low. The number of DR patients increase with increase in the diabetic population, especially in developing countries like India where there is resource scarcity. Timely treatment can prevent irreversible vision loss from diabetic retinopathy.
Risk factor of diabetic retinopathy are
- Duration of diabetes
- Uncontrolled fluctuation of blood sugar level
- Uncontrolled Hypertension
- Raised Serum lipids and cholesterol
- Other factors like pregnancy, nephropathy etc.,
Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Initial changes are called Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR) which later progresses to the Proliferative stage of Diabetic retinopathy (PDR). NPDR stage further divided as mild, moderate, severe, & very severe stage of NPDR. In any of these stages the central retina, which is important for the central sharp vision, can be affected by the leakage of the weakened blood vessels leading to the edema/swelling – called Clinically Significant Macular edema (CSME), which will damage central vision
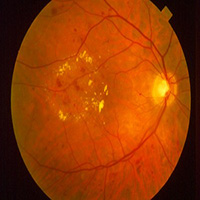
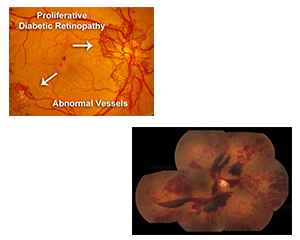
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
PDR is characterised by the growth of new blood vessels in response to tissue hypoxia. The affected patient may see floaters or feel blurring of vision or distorted vision. These symptoms are due to bleeding from the abnormal blood vessels i.e. vitreous hemorrhage or due to the tractional retinal detachment. Vision can also get damaged due the blood vessel growth in the iris (Neovascular glaucoma).
Known diabetic patients are advised to get annual dilated eye examination regularly even without any symptoms as these changes can be identified by the Ophthalmologist in early stages and can be prevented the possible loss of vision.

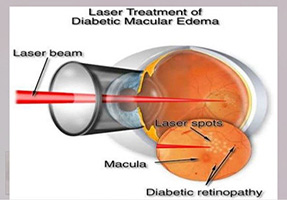
Laser photocoagulation
In the last 40-50 years, only LASER treatment could save more than 50% of the vision in these patients. Lasers will convert hypoxic retina into anoxic retina and hence reduces abnormally grown blood vessels over a period of time. This reduces possible bleeding and pull on the retina. Laser also seals the leaking blood vessels to reduce the swelling in the central retina.
Intravitreal injections
However, advanced research helped the treatment further by the newer pharmacotherapy i.e. intra-vitreal injections. This treatment dramatically improved the outcome of these patients. The only drawback of these treatments in India is affordability among many poor Indian communities. The use of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) antibodies has been shown to be very useful in the treatment of many vascular leaking conditions including diabetic retinopathy. They are useful for both macular edema and proliferative retinopathy. The most common anti-VEGFs are BEVACIZUMAB (Avastin), RANIBIZUMAB (Lucentis/Accentrix, Razumab), and AFLIBERCEPT (Eylea).
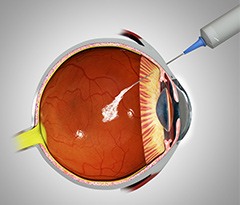
The other injections which help in reducing retinal/macular edema are STEROIDS. The 2 steroid injections commonly & safely used are TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE & OZURDEX (Dexamethasone sustained release implant. However these steroid injections can have few side-effects (like cataract, Glaucoma) which need monitoring & treatment whenever necessary.
The surgical treatment may be necessary when there is organised blood in vitreous, tractional retinal detachment/pull involving important part of retina. The current technology is extremely good with suture-less vitrectomy (23/25/27G Micro-Incision Vitrectomy surgery-MIVS) and the results will be better if done early.
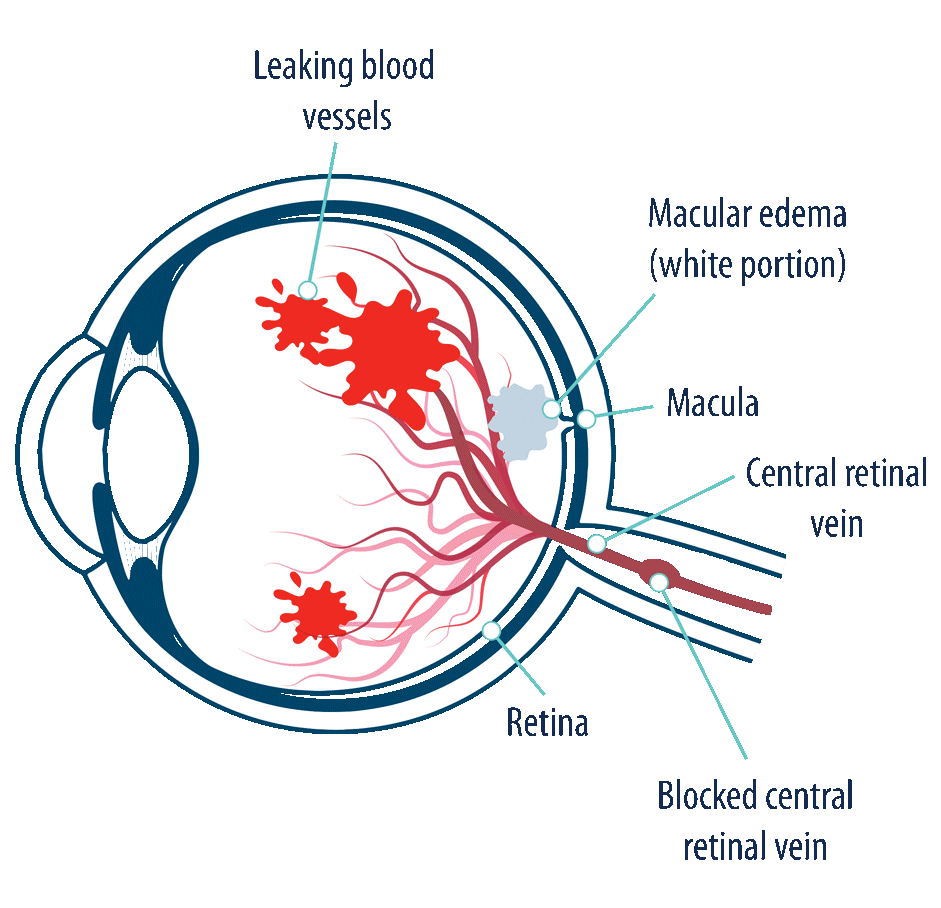
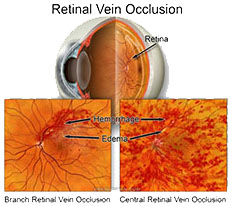
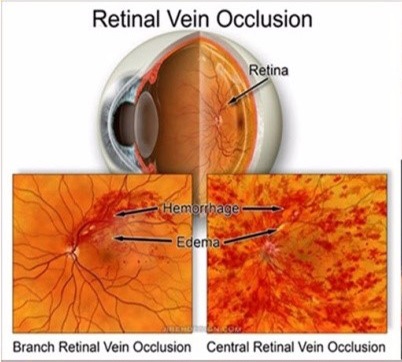
- It is an eye condition commonly seen in the retina clinic. It is the second most common cause of visual loss due to retinal vascular disease.
- It is essentially a blockage of the circulation that drains blood from the retina.
- Can affect the central retinal vein or a branch retinal vein or any of the tributaries also.
- Males and females are affected equally.
Symptoms
- Sudden painless loss of vision
- Usually unilateral
Complications of vein occulsion
- The most important complication is NEOVASCULARIZATION.
- New vessels develop in about 40% of cases due to capillary nonperfusion.
- Usually seen in the first 6-12 months after occlusion.
- It can lead to vitreous hemorrhage, tractional retinal detachment or Neovascular glaucoma.
Who are at Risk?
How do we diagnose it?
- Ageing-most occlusions are seen in patients over 50, although younger patients with hyperviscosity disorders present early.
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes mellitus
- High cholesterol
- Smoking
- Hyperhomocystenemia
- Protein C or protein S deficiency,Anti phospholipid antibodies-conditions which cause slowing/sludging of the circulation called Hyperviscosity state.
- Activated protein C resistance(factor V Leiden)
- Inflammatory and infectious conditions which cause vasculitis also predispose to vein occlusions
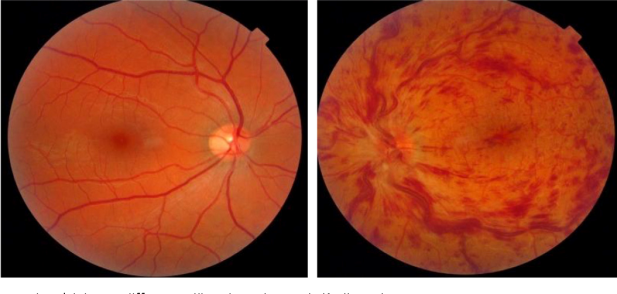
The doctor will evaluate the fundus after instillation of dilating drops.
Appearance of multiple haemorrhages,blocked dilated blood vessels and edema (swelling) in the macula are assessed.
The most important reason for poor vision is swelling in the central part of retina (macula).
Intravitreal injections
However, advanced research helped the treatment further by the newer pharmacotherapy i.e. intra-vitreal injections. This treatment dramatically improved the outcome of these patients. The only drawback of these treatments in India is affordability among many poor Indian communities. The use of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) antibodies has been shown to be very useful in the treatment of many vascular leaking conditions including diabetic retinopathy. They are useful for both macular edema and proliferative retinopathy. The most common anti-VEGFs are BEVACIZUMAB (Avastin), RANIBIZUMAB (Lucentis/Accentrix, Razumab), and AFLIBERCEPT (Eylea).
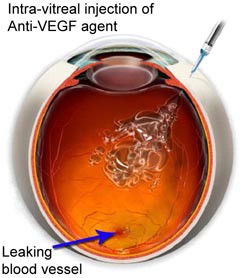
- OZURDEX is a long acting steroid with fewer side effects and is effective in patients who have not responded well to antiVEGFs.
Laser photocoagulation
Helps in preventing further vision loss by stabilizing the new vessel formation
Surgery
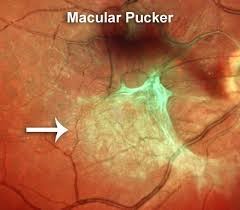
Sometimes, following venous occlusive disease, scar tissue can form on the retinal surface called as Epiretinal membrane or macular pucker. This causes distorted vision which cannot be improved with laser or pharmacologic treatment. Vitrectomy surgery is done for membrane peeling.
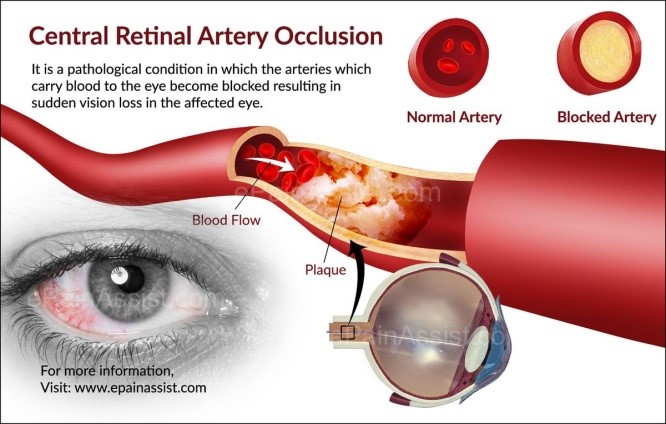
IT IS AN OPHTHALMIC EMERGENCY, wherein the artery or branch is blocked, thereby stopping blood flow to the retina.Presents as sudden painless loss of vision in one eye.
Treatment
- Should be administered within half an hour to have better prognosis.
- It involves ocular massage, anterior chamber paracentesis, hyperbaric oxygen,thrombolytic therapy.
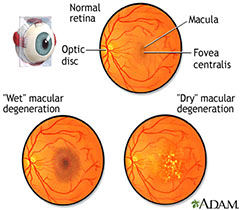
The retina is the light-sensitive tissue lining the back of the eye.
The macula is the part of the retina that is responsible for your central vision, allowing you to see fine details clearly.
Many older people develop macular degeneration as part of the body’s natural aging process. This is called age-related macular degeneration(AMD).

Symptoms
- Blurred vision
- Distortion of image (metamorphopsia)
- Loss of central vision

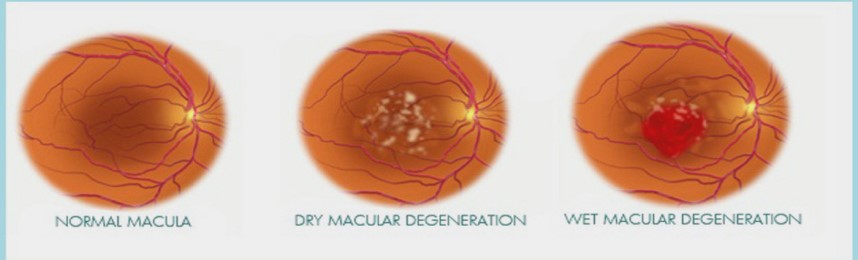
Types of AMD
- DRY AMD: Characterized by gradual loss of central vision due to drusen deposits.
- WET AMD:Seen in about 10% patients, leading to abnormal blood vessels below the retina called CHOROIDAL NEOVASCULAR MEMBRANE.
Diagnosis
Any early distortion of images or vision disturbances should be reported to the ophthalmologist.
- Dilated fundus evaluation
- Amslers charting
- OCT
- FFA AND ICG-To locate leaky vessels.
There is no treatment for Dry AMD.
Good diet, healthy lifestyle, cessation of smoking, multivitamin and antioxidant capsules help in delaying progression.
Wet AMD is best managed when detected early.
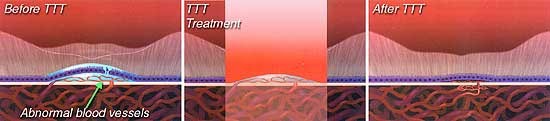
Trans pupillary thermotherapy(TTT)
Uses a long pulse 810nm near infrared diode laser which closes the CNVM.
Photodynamic therapy(PDT)
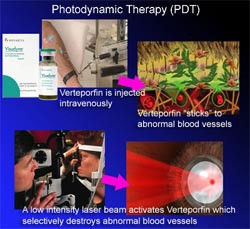
Photosensitizer dye(VERTEPORFIN) accumulates in abnormal tissue which is then damaged by appropriate wavelength light This is more specific than laser treatment,as it targets only photosensitive dye.
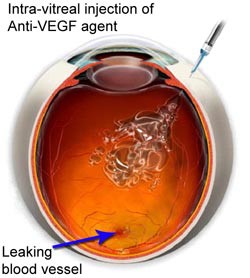
Intravitreal injections
Currently, the most common and effective clinical treatment for Advanced Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration is anti-VEGF therapy – which is periodic intravitreal (into the eye) injection of a chemical called an “anti-VEGF”. Eylea-Aflibercept (Eylea/VEGF Trap-Eye from Regeneron/Bayer) is one form of anti-VEGF therapy, and recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration. Other variants of anti-VEGF injections include ranibizumab (Lucentis, made by Genentech/Novartis), and bevacizumab (off label Avastin from Genentech). Each of these chemicals works in a different way to inhibit blood vessel growth.
Surgical options
- Vitreoretinal surgery and vitrectomy have had important developments, mostly due to advances in sutureless transconjunctival vitrectomy, use of dyes, tamponade agents and new equipments.
- Meanwhile, a different management paradigm for AMD was established with macular translocation.
- Novel surgical approaches for AMD are under scrutiny: the association of submacular surgery with pigment cell transplantation, the use of adjuncts, such as recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (r-TPA) for subretinal hemorrhages displacement combined with anti-VEGF treatment.
- Submacular surgery
- Macular translocation
- However, because of its higher risk of complications, its popularity has waned with the wider availability of photodynamic therapy and the introduction of intravitreal anti-VEGF agents.
- Nonetheless, they remain potentially useful treatment options, even if their role in the management of AMD is neither established nor consensual.
- Low visual aids and visual rehabilitation
- Magnifying glasses,telescopes,bionic eye
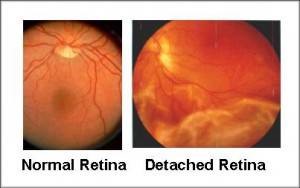
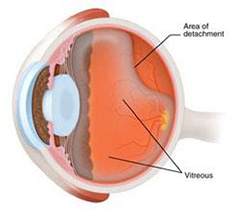
Retina is the light sensitive innermost layer of the eye. Detachment refers to the separation of this layer from its normal position.
- Floaters or cobwebs in the eye
- Flashes of light,shadows or curtains in the field of vision
- Sudden painless loss of vision

Instillation of dilating drops
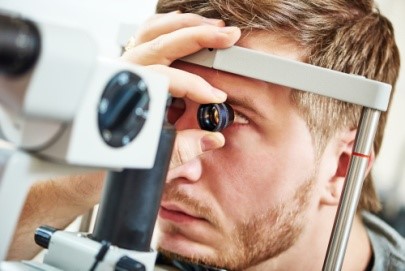
The retina specialist will examine the eye after instillation of dilating drops.
Ultrasound scan
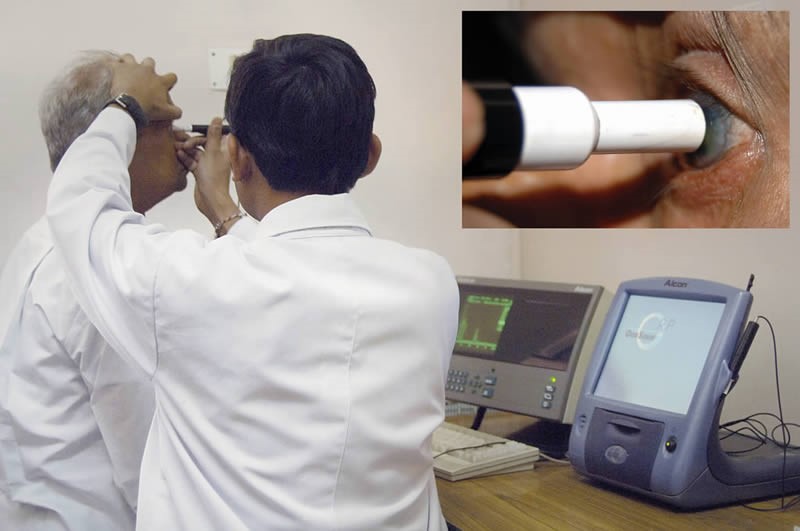
Ultrasound scan (B SCAN) is done to assess the detachment.
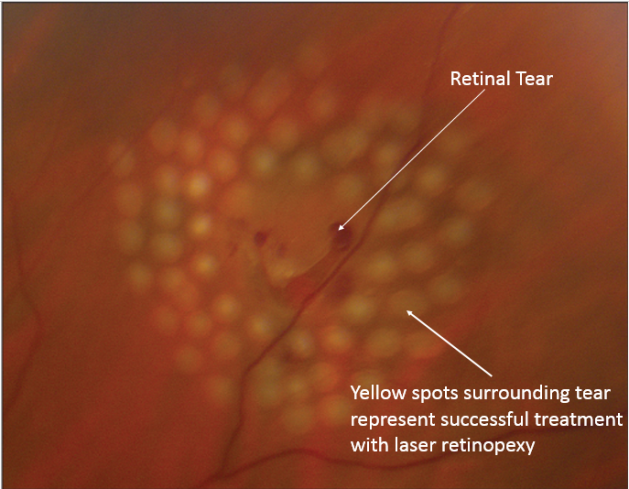
Laser for retinal holes
Laser is used to create tiny burns around the retinal tears. The healing that occurs after the laser burns essentially spot-welds the retina down and prevents the tear from causing a retinal detachment. If not treated, fluid can leak through these tears and cause the retina to detach, leading to vision loss.
What happens during laser treatment?
- Your pupils will be dilated
- Local anesthetic drops will be placed in your eye.
- If an indirect laser is used you will be positioned so that that you're lying flat for the laser treatment.
- If a microscope is used, a special contact lens will be placed on your eye to hold your lids apart and focus the laser.
- During treatment, you will see bright flashes of light.
- The treatment usually takes 5 - 10 minutes.
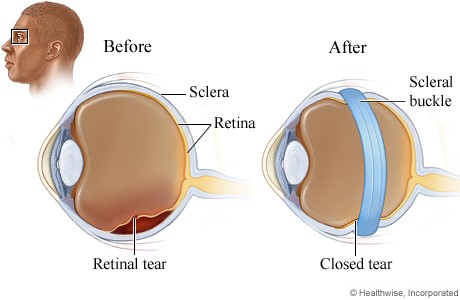
Scleral buckling
In this a silicone encircling band or sectoral buckle is sutured to the sclera which indents the outside of the eye towards the detached retina.
Pneumoretinopexy
Pneumoretinopexy is a method of treating selected cases of retinal detachments.A gas bubble is injected into the eye after applying cryo spots to the area of retinal tear. The patient is expected to maintain a certain posture after the procedure for about a week to ten days. Also, he is not allowed to travel by air during this period.
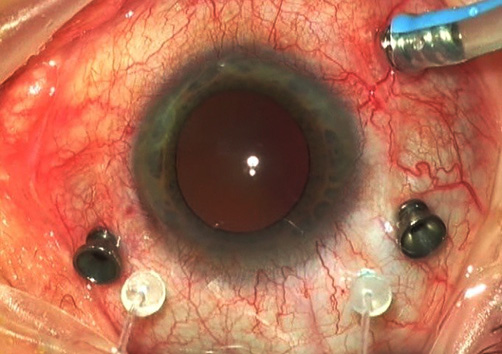
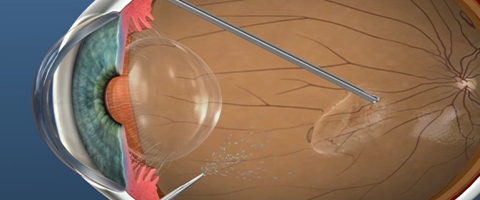
Vitrectomy
- Bangalore Nethralaya has the latest and the most sophisticated surgical equipments.
- Micro incision and sutureless (23/gauge) vitrectomy(MIVS) is performed using the CONSTELLATION® machine.
- The advantages of this surgery is the absence of stitches in the eye.
- Hence the post-operative recovery is faster.
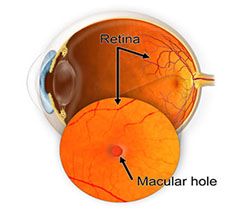
WHAT CAUSES A MACULAR HOLE??
- Idiopathic
- Trauma
- High myopia
- Macular edema
WHAT ARE THE SYSMPTOMS?
- Mild loss of central vision(esp in early stages)
- Metamorphopsia(distortion of image)
Fundus examination
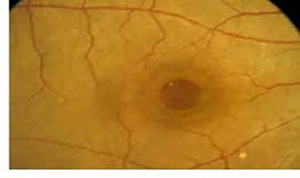
OCT
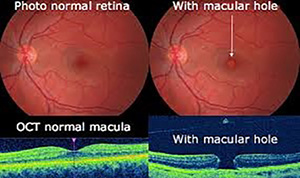
Spontaneous resolution
This is seen most commonly in stage 1 and stage 2 holes.
Surgery
PARS PLANA VITRECTOMY with ILM peeling with gas tamponade.
-
Diabetes damages the blood vessels in the retina, makes them leaky, giving rise to haemorrhage and therefore vision loss
-
Yearly basis in case of good control and normal retina or more frequently as advised by the ophthalmologist.
-
Vitamin A deficiency, retinitis pigmentosa, rod dystrophies
-
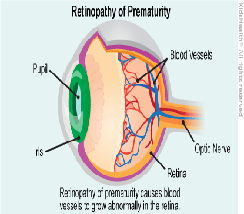
There is a condition called retinopathy of prematurity which causes abnormal blood vessels in retina leading to visual loss and hence needs to be detected early.This can lead to irreversible permanent loss of vision which can be prevented with simple lasers, if detected early
-
Whenever there is fluid collected in the central of retina (macula) due to various conditions like diabetes, hypertension, vein occlusion, etc, or in conditions like age related macular degeneration, there is profoynd visual loss, which can be treated with intravitreal injections/ IVTA/ dexamethaxone implant.
-
Laser helps in reducing the growth of abnormal blood vessels and hence stops bleeding. Laser also helps in reducing leakage of fluid from the weakened blood vessels which prevents vision loss. Laser is mandatory treatment whenever there is abnormal blood vessel growth in the retina.
-
Majority of the retinal condition improves to the extent possible gradually and slowly. It varies depending on the condition, systematic control and type of treatment. We can expect significant possible improvement on one month after the surgical intervention in majority of the conditions.